The sample paper is one of the best resources for the student to prepare for the
exam. These help the student to get a prior experience before they attempt for
the final exam also, they will know if they are prepared for the exam
completely or not. They can test their knowledge for all these subjects and get
confident about the answer. if any discrepancies occur in the written answer,
they can focus more on such a question, so that there are no mistakes happening
in the final paper. they can also mark themselves for correct and wrong
answers.
Structure
of CBSE Class 12th Biology Model Paper 2020
Biology
the paper will be of three hours and a total of 70 marks. the paper will consist of 27 questions all divided
into five sections.
Section
A: Multiple choice questions.
There
will be a very multiple choice type question
1 to 5 in this section. each
question will have 1 mark.
Section
B: Short answer questions.
There
will be Short answer questions of 6 to 12, each question will have 2 marks.
Section
C: short answer type II questions
There
will be short answer type questions of 13 to 21, each question will have 3
marks.
Section
D: case-based short answer type question
There
will be case-based short answer type question of 22 to 24, each The question
will have 3 marks each.
Section
E: Long answer type question
There
will be also long answer type question of 25 to 27, each The question will have
5 marks each
There
is no overall choice in the question paper. However, internal choices are
provided in two questions of one mark, one question of two marks, two questions
of three marks and all three questions of five marks. An examinee is to attempt
any one of the questions out of the two given in the question paper with the
same question number.
SECTION – A
1. Androgens
are synthesize by:
a.) Sertoli Cells
b.) Leydig cells
c.) Seminal vesicles
d.) Bulbourethral
gland
OR
A procedure
that finds use in testing for genetic disorders, but is also misused
for foeticide is:
a.) Lactational
amenorrhea
b.) Amniocentesis
c.) Artificial insemination
d.) Parturition
2. Transplantation of tissues/organs to save certain
patients often fail due to the rejection of such tissues/organs in the patient’s
body. Which type of immune response Is it responsible for such rejection?
a.) auto-immune response
b.) humoral
immune response
c.) physiological
immune response
d.) cell-mediated immune response
OR
Which
of the following are the correct reasons for Rheumatoid arthritis?
i.) Lymphocytes become more active
ii.) Body attacks self cells
iii.) More antibodies are produced in the
body
iv.) The ability to differentiate pathogens or foreign
molecules from self cells is lost
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below:
a.) i
and ii
b.) iii
and iv
c.) i and iii
d.) ii and
iv
3. Name the
enzymes 'P' and 'Q' that carry out the following processes
a.) Enzyme P-Exonuclease and Enzyme Q-Permease
b.) Enzyme P-Exonuclease and Enzyme Q-
Ligase
c.) Enzyme P-Endonuclease and Enzyme Q-
Permease
d.) Enzyme P-Endonuclease and Enzyme Q-Ligase
4. A biotechnologist wanted
to create a colony of E.coli possessing the plasmid pBR322, sensitive to Tetracycline. Which one of the following
restriction sites would he use
to ligate a foreign DNA?
a.) Sal I
b.) Pvu I
c.) EcoRI
d.) Hind III
5. Most important cause of biodiversity loss is
a.) Overexploitation of economic species
b.) Habitat loss
and fragmentation
c.) Invasive species
d.) Breakdown of plant-pollinator relationships
SECTION B
6. How does an encysted Amoeba reproduce on the return of favorable
2 conditions?
OR
What are gemmules and conidia? Name one organism each in which these
are formed?
7. Name any two copper-related IUD’s. Explain how it acts as a
contraceptive?
8. Why is it not possible
to study the inheritance pattern of traits
in human beings, the same way as it is done in pea plants? Name the alternate method employed for such an
analysis of human traits.
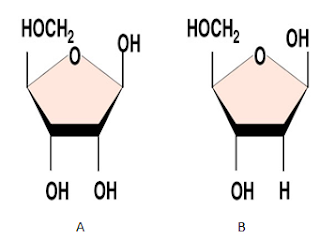
9. Carefully examine
structures A and B of pentose sugar given below.
Which one is more reactive? Give reasons.
10. Name the technology and the procedure involved which can help a scientist
recover virus-free sugarcane plants from diseased canes for his crop breeding experiments.
11. Explain the events that occur in the host cell on the introduction of nematode-resistant
gene into the tobacco plant by using Agrobacterium
vectors.
12. Construct a pyramid of biomass starting
with phytoplankton. Label three trophic levels. Is the pyramid upright
or inverted? Justify your answer.
SECTION C
13. Draw a well-labeled diagram of L.S of a pistil showing the passage of growing
of pollen tube up to its destination.
14. How does the gain or loss of chromosome(s) take place in humans? Describe one example each of chromosomal disorder
along with the symptoms
involving an autosome and a
sex chromosome.
OR
A small stretch of DNA that
codes for a polypeptide is given below
3'---
--- --- --- CAT CAT AGA TGA AAC--- --- --- --- 5'
a.) Which type
of mutation could have occurred in each type resulting in the following mistakes during replication of the above original sequence?
i. 3`…
… … …CAT CAT AGA TGA ATC… … …5` ii. 3`…
… … …CAT ATA GAT GAA AC… … … 5`
b.) How many amino acids will
be translated in each of the above two cases?
15. “Apomixes
is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction
16.
a.) State the hypothesis which S.L. Miller tried to prove
in the laboratory with the help of the set up given above.
b.) Name the organic
compound observed by him in the liquid water after
running the above experiment.
c.) A scientist simulated
a similar setup and added
CH4, NH3 and water vapor at 800 ℃. Which important component is missing in his experiment?
17. a.)
FILL IN
THE BLANKS PROVIDED
|
Amino acid Phe Val
|
DNA
Code in Gene AAA CAC
|
Codon
in mRNA (i) (ii)
|
Anticodon
in tRNA (iii) (iv)
|
b.) A polypeptide consists of 14 different amino acids.
i) How many base pairs must be there in the processed mRNA that
codes for this polypeptide?
ii) How many different
types of tRNA are needed for the synthesis of this polypeptide?
18. How can inbreeding be both advantageous and disadvantageous in cattle
breeding program? (Mention any two advantages and two
disadvantages )
19. “Specific Bt Toxin gene is incorporated into the cotton plant so as to control the infestation of Bollworm”. Mention the organism
from which the gene was isolated and explain its mode of action.
20. State any two criteria
for determining biodiversity hotspots. Name any two hotspots designated in India.
OR
Differentiate between
in-situ and ex-situ
approaches for conserving
biodiversity. Give an example for each.
21. When the gene product is required in large amounts, so transformed bacteria with the plasmid
inside the bacteria
are cultured on a large scale in an industrial fermenter which then synthesizes its protein.
This product is extracted
from the fermenter for commercial use.
a.) Why is the used medium drained out from one side while fresh medium
is added from the other?
b.) List any four optimum conditions for achieving the desired product
in a bioreactor.
SECTION D
22.
a.) About 300 million spermatozoa may be present in a human male ejaculation at one time. Calculate how many spermatocytes will be involved to
produce this number of spermatozoa.
b.) How many spermatids will be
formed?
c.) How many chromatids are found during Oogenesis
in Primary oocyte and First polar body in a human female?
23. Large
quantities of sewage are generated every day in cities and towns, which is
treated in Sewage
Treatment Plants (STPs)
to make it less polluting.
Given below is the flow diagram of one of the stages of STP.
Observe the given flow
diagram and answer the questions accordingly.
a.) Why primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks?
b.) What is the scientific term used for the sediment
formed? Mention its significance.
c.) Explain
the final step resulting
in the formation of biogas in the large tank before the treated effluent is
released into water bodies.
24.
Observe the diagram of the catalytic
converter and answer the questions which follow.
a.) Name any two metals used as a catalyst in
the catalytic converter.
b.) Name the gases released after passing the exhaust hydrocarbons through the catalytic converter.
c.) Which other poisonous gas is missing
in the exhaust pollutant of an
automobile in the above diagram?
SECTION E
25. Certain phenotypes in the human
population are spread
over a gradient and reflect the contribution of more than two genes. What is the term used for the types of inheritance? Describe it with the help of an example in the human
population.
OR
Summarize the process
by which the sequence of DNA bases in the Human Genome Project was determined
using the method developed
by Frederick Sanger. Name a free-living non-pathogenic nematode
who’s DNA has been sequenced.
26. a.) What is mutation
breeding? Give an example of a crop and disease
to which resistance was induced by mutation.
b.) Differentiate
between pisciculture and aquaculture.
OR
a.) If a patient
is advised anti-retroviral drugs, which infection is he
suffering from? Name the causative
organism.
b.) How do vaccines prevent subsequent microbial infections?
c.) How a cancerous cell differs from the normal cell?
d.) Many microbial pathogens
enter the gut of humans along with food. Name the physiological
barrier that protects the body from such
pathogens.
27. “Indiscriminate human activities have strengthened the greenhouse effect
resulting in Global Warming.” Give the relative contribution of various Green House Gases in the form of a pie chart and explain
the fate of the energy of sunlight reaching
the earth’s surface
contributing to Global Warming.
OR
Given
below is a table depicting population
interactions between species A and species B.
Type
of interaction
|
Species
A
|
Species
B
|
(a)
|
(-)
|
(+)
|
(b)
|
(+)
|
(-)
|
Name
the two types of population interactions (a)
and (b) depicted in the above table.
Justify
giving three reasons, how the type of
interaction (b) is important in an
ecological context.